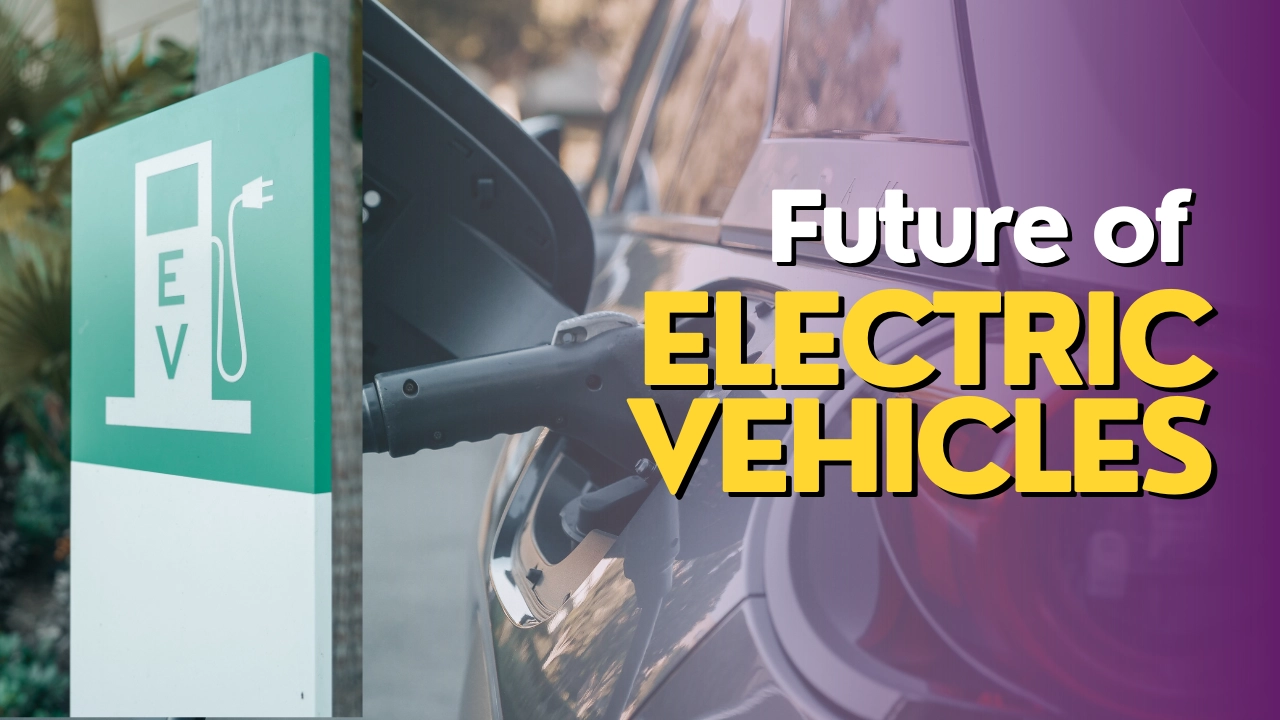
India is the world’s third-largest consumer of crude oil, importing nearly 80% of its crude oil requirements. The high dependence on imported crude oil has made India vulnerable to fluctuations in global crude oil prices. Additionally, the transportation sector is the second-largest consumer of energy in India, accounting for nearly 40% of total oil consumption. Therefore, there is a pressing need to transition to a cleaner and more sustainable mode of transportation, and electric vehicles (EVs) hold immense potential in this regard. In this blog, we can discover the destiny of electrical cars in India.
Current State of EVs in India
The Indian government has been promoting the adoption of electric vehicles in the country since 2013. However, the progress has been slow, with EVs accounting for only 1% of total vehicle sales in India in 2020. The main challenges in the adoption of EVs in India include high upfront costs, lack of charging infrastructure, and range anxiety. Despite the challenges, there has been some progress in the EV market in India. The government has announced various incentives and schemes to encourage the adoption of EVs, such as the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of (Hybrid &) Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme and the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP). Additionally, several Indian companies, such as Tata Motors, Mahindra & Mahindra, and Hero Electric, have launched EVs in the Indian market.
Future of EVs in India
The future of EVs in India looks promising, and several factors are expected to drive the growth of the EV market in India in the coming years.
Government Support
The Indian government has been actively promoting the adoption of EVs in the country and has announced several initiatives to support the EV market. The FAME scheme, which provides financial incentives for the purchase of EVs, has been extended until 2024. Additionally, the government has announced plans to set up EV charging stations across the country, with a target of 69,000 charging stations by 2025.
Falling Battery Prices

One of the main factors that have hindered the adoption of EVs in India is the high cost of batteries. However, the prices of lithium-ion batteries, which are used in EVs, have been falling rapidly in recent years. According to a report by Bloomberg New Energy Finance, the cost of lithium-ion batteries is expected to fall by 58% by 2030, making EVs more affordable.
Environmental Concerns
India is one of the most polluted countries in the world, and air pollution has become a major public health issue in the country. The transportation sector is one of the main contributors to air pollution in India. Therefore, there is a growing awareness of the need to transition to cleaner modes of transportation, and EVs are seen as a viable alternative.
Technological Advancements
The EV market has been witnessing significant technological advancements, which are expected to make EVs more efficient, affordable, and convenient. For example, the development of solid-state batteries, which offer higher energy density and faster charging times than lithium-ion batteries, is expected to revolutionize the EV market.
Challenges in the Adoption of EVs in India
While the future of EVs in India looks promising, there are still several challenges that need to be addressed to accelerate the adoption of EVs in the country.
Charging Infrastructure
The lack of charging infrastructure is a major bottleneck in the adoption of EVs in India. There is an urgent need to develop a robust network of charging stations across the country to support the widespread adoption of EVs. While the government has initiated several measures to increase the number of charging stations, there is still a long way to go to ensure that there are sufficient charging stations in all regions of the country. Additionally, there needs to be a standardization of charging protocols to enable easy interoperability of EVs and charging stations.
Affordability
The high cost of EVs compared to conventional vehicles is another major challenge. While the cost of EVs has been declining, they are still more expensive than petrol or diesel vehicles. The affordability of EVs is critical for their adoption in India, where a large proportion of the population is price-sensitive. The government’s FAME scheme has provided incentives for the purchase of EVs, but more needs to be done to reduce the upfront cost of EVs and make them more affordable for the masses.
Range Anxiety
Range anxiety, or the fear of running out of charge while driving, is a significant concern for potential EV buyers. The limited range of EVs, coupled with the lack of charging infrastructure, makes long-distance travel challenging. While the range of EVs has been increasing in recent years, it is still not on par with conventional vehicles. Additionally, the lack of a standardized charging protocol and the unavailability of charging stations in certain regions further exacerbate the range anxiety issue.
Battery Disposal
Battery disposal is a critical issue that needs to be addressed in the adoption of EVs in India. Lithium-ion batteries, which are used in most EVs, contain toxic chemicals and heavy metals that can cause environmental harm if not disposed of properly. Therefore, there needs to be a mechanism to ensure the safe disposal and recycling of EV batteries to minimize their environmental impact.
Consumer Awareness
Finally, consumer awareness and education are critical for the widespread adoption of EVs in India. Many consumers are still unaware of the benefits of EVs and have misconceptions about their performance and affordability. Therefore, there needs to be a concerted effort to educate and create awareness among consumers about the benefits of EVs, including their lower operating costs, lower environmental impact, and better performance compared to conventional vehicles.
Conclusion:
Electric vehicles have the potential to transform India’s transportation sector and help the country meet its energy security, pollution, and congestion challenges. While the future of EVs in India looks promising, there are several challenges that need to be addressed to accelerate their adoption. The government, private sector, and other stakeholders need to work together to develop a robust charging infrastructure, reduce the upfront cost of EVs, address range anxiety concerns, ensure safe battery disposal, and create consumer awareness. If these challenges are addressed, EVs could become a major contributor to India’s sustainable and inclusive growth.