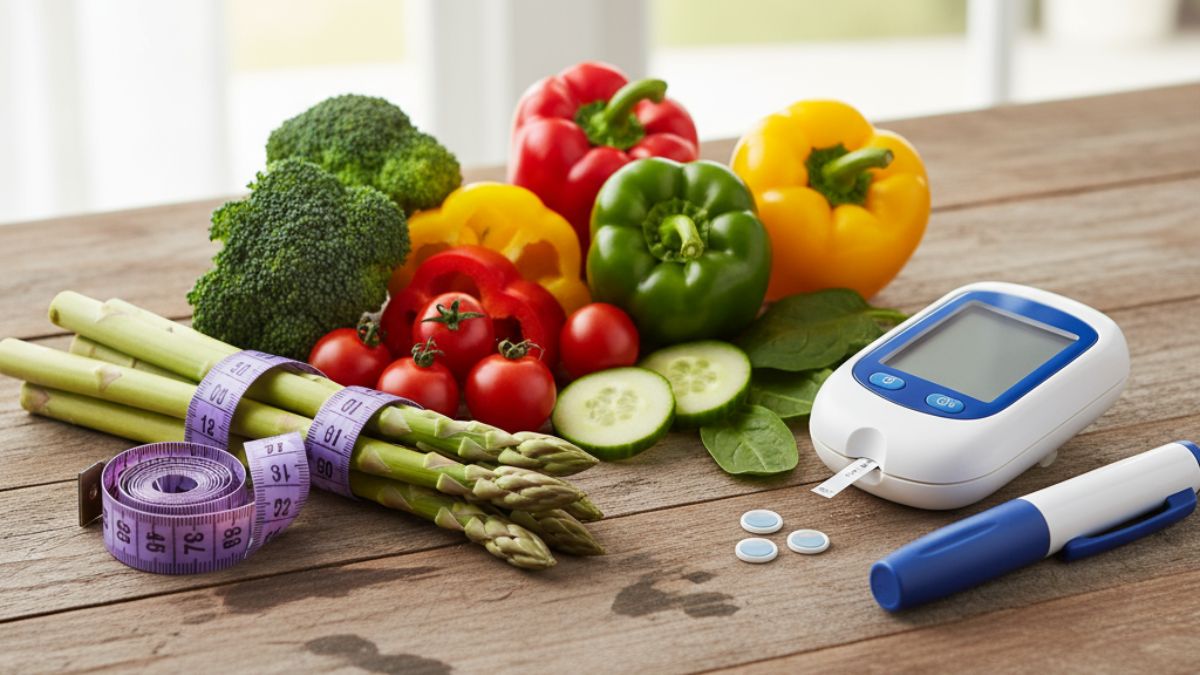
Diabetes, including type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes, poses a serious health risk when sugar levels run high and insulin function falters. Protecting yourself from diabetes begins with understanding risk factors and adopting proven lifestyle changes in diet, exercise, and monitoring to maintain healthy blood glucose levels.
Understanding Diabetes: Type 1 Diabetes vs. Type 2 Diabetes
Before diving into prevention tactics, it’s essential to distinguish between the two main forms of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. It often manifests in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy to regulate blood sugar.
- Type 2 Diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough. It is strongly linked to poor diet, physical inactivity, and obesity, but it can often be prevented—or even reversed—through targeted lifestyle changes.
Both types share the hallmark of elevated blood sugar, but their causes and treatments differ. Prevention strategies focus mainly on thwarting type 2 diabetes, although maintaining healthy habits benefits everyone.
Adopt a Balanced, Low-Sugar Diet
Slashing refined carbohydrates and added sugars from your meals is a powerful way to stabilize blood glucose levels and protect against type 2 diabetes. Follow these steps to transform your eating habits:
- Embrace Whole Foods
Fill your plate with colorful vegetables, fresh fruits, whole grains, legumes, lean proteins, and healthy fats (avocado, nuts, seeds). These nutrient-dense foods digest slowly, preventing dangerous blood sugar spikes. - Eliminate Sugary Drinks
Sweetened sodas, energy drinks, and fruit juices pack extreme amounts of sugar. Replace them with water, herbal teas, or infused water to stay hydrated without harming your insulin sensitivity. - Mind Your Carbohydrate Portions
Use the plate method: half non-starchy veggies, one-quarter lean protein, and one-quarter whole grains or starchy vegetables. This approach helps you monitor carb intake without counting grams obsessively. - Choose Low Glycemic Index (GI) Foods
Foods like oats, barley, sweet potatoes, and most fruits have a low GI, meaning they elevate blood sugar gradually. Incorporate these staples to maintain stable glucose and reduce insulin demand. - Plan Balanced Snacks
Combine protein or healthy fat with a small portion of complex carbs—such as apple slices with almond butter or Greek yogurt with berries—to curb mid-afternoon hunger and prevent sugar cravings.
Maintain Regular Physical Activity
Exercise is a cornerstone of diabetes prevention and control, enhancing cellular uptake of glucose and improving insulin sensitivity:
- Aim for Consistency
Strive for at least 150 minutes per week of moderate-intensity cardiovascular exercise (brisk walking, swimming, cycling). Breaking this into 30-minute sessions on five days a week yields substantial benefits. - Include Strength Training
Muscle-building exercises—using weights or bodyweight moves like squats, lunges, and push-ups—twice weekly increase lean muscle mass, which burns more glucose at rest. - Incorporate Daily Movement
Reduce sedentary time by standing up every hour, taking the stairs instead of the elevator, parking farther away, or walking during phone calls. Small bursts of activity throughout the day add up. - Find Enjoyable Activities
Dancing, hiking, team sports, and yoga are excellent options. Enjoyment increases adherence, making it more likely you’ll stick with your routine long term.
Monitor Blood Glucose and Manage Insulin Needs
Early detection and vigilant monitoring empower you to act before diabetes worsens:
- Use a Glucometer
Check fasting and post-meal glucose levels to identify patterns and make informed dietary adjustments. Many models connect to smartphone apps, simplifying data tracking. - Explore Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM systems provide real-time glucose readings, alarms for highs and lows, and trend graphs. Discuss CGM options with your healthcare provider, especially if you have prediabetes or a family history of type 1 diabetes. - Follow Prescribed Insulin Regimens
For those with type 1 diabetes, adhering strictly to insulin dosing schedules and adjusting based on glucose readings is vital to avoid dangerous highs and lows. - Track HbA1c Levels
Annual HbA1c tests reveal your average blood sugar over three months. Strive for an HbA1c below 6.5% to minimize the risk of complications.
Manage Stress and Prioritize Sleep
Chronic stress elevates blood sugar and disrupts insulin action. Poor sleep exacerbates these effects:
- Adopt Relaxation Techniques
Practice deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, or guided imagery for 10–15 minutes daily. These practices lower cortisol and protect metabolic health. - Establish a Sleep Routine
Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep per night. Maintain consistent bed and wake times, create a dark, cool bedroom environment, and avoid screens at least one hour before bedtime. - Limit Caffeine and Alcohol
Both substances can interfere with sleep and blood glucose control. Consume in moderation, and avoid caffeine after mid-afternoon.
Regular Health Check-Ups and Screening
Preventive healthcare is your ally in the fight against diabetes:
- Annual Screening
If you are over 45 or have risk factors—such as obesity, family history, or hypertension—undergo yearly fasting glucose and HbA1c tests. - Monitor Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
High blood pressure and dyslipidemia strain blood vessels and worsen diabetes complications. Keep these parameters under control through diet, exercise, and medication if needed. - Consult Specialists
A registered dietitian can craft personalized meal plans, and a certified diabetes educator can guide you through glucose monitoring and lifestyle adjustments.
Building a Diabetes-Resilient Lifestyle
By implementing these strategies, you forge a powerful defense against type 2 diabetes and support overall well-being. Key takeaways include:
- Adopting a balanced, low-sugar diet rich in whole foods
- Maintaining regular physical activity and strength training
- Monitoring blood glucose levels and managing insulin needs
- Prioritizing stress management and restorative sleep
- Engaging in routine health screenings for early detection
Empower yourself today with these proven tactics and take control of your health—because conquering diabetes begins with the choices you make every day.